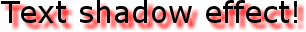CSS

HTML + CSS + JavaScript
结构 + 表现 + 动作
1、什么是CSS
如何学习
- CSS是什么
- CSS怎么用(快速入门)
- CSS选择器(重点+难点)
- 美化网页(文字,阴影,超链接,列表,渐变…)
- 盒子模型
- 浮动
- 定位
- 网页动画(特效效果)
1.1、什么是CSS
Cascading Style Sheet层叠样式表
CSS:表现(美化网页)
字体,颜色,边距,高度,宽度,背景图片,网页定位,网页浮动
1.2、发展史
CSS1.0
CSS2.0:DIV(块)+CSS,HTML与CSS结构分离的思想,网页变得简单,SEO
CSS2.1:浮动,定位
CSS3.0:圆角、阴影、动画…浏览器兼容性~
1.3、快速入门
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--规范,<style>可以编写CSS的代码,每一个声明最好以“;”结尾
语法:
选择器{
声明1;
声明2;
声明3;
}
-->
<style>
h1{
color: crimson;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>CSS测试</h1>
</body>
</html>
|
建议使用这种规范

CSS的优势:
1、内容和表现分离;
2、网页结构表现统一,可以实现复用
3、样式十分的丰富
4、建议使用独立于html的css文件
5、利用SEO,容易被搜索引擎收录!
1.4、CSS的3种导入方式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--内部样式-->
<style>
h1{
color: green;
}
</style>
<!--外部样式-->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css" />
</head>
<body>
<!--优先级:就近原则-->
<!--行内样式:在标签元素中,编写一个style属性,编写样式即可-->
<h1 style="color: red">这是标签</h1>
</body>
</html>
|
拓展:外部样式两种方法
Link
1
2
| <!--外部样式-->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css" />
|
@import是CSS2.1特有的!
1
2
3
4
| <!--导入式-->
<style>
@import url("css/style.css");
</style>
|
1、标签选择器:选择一类标签 标签{}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
h1{
color: orange;
background: blue;
border-radius: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>标签选择器</h1>
</body>
</html>
|
2、类 选择器class:选择所有class一致的标签,跨标签,格式:.类名{}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.demo1{
color: blue;
}
.demo2{
color: red;
}
.demo3{
color: aqua;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class = "demo1">类选择器:demo1</h1>
<h1 class="demo2">类选择器:demo2</h1>
<h1 class="demo3">类选择器:demo3</h1>
</body>
</html>
|
3、id 选择器:全局唯一,格式:#id名{}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
#demo1{
color: aqua;
}
.demo2{
color: red;
}
#demo2{
color: orange;
}
h1{
color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 id="demo1">id选择器:demo1</h1>
<h1 class="demo2" id = "demo2">id选择器:demo2</h1>
<h1 class="demo2">id选择器:demo3</h1>
<h1>id选择器:demo4</h1>
<h1>id选择器:demo5</h1>
</body>
</html>
|
优先级:id > class > 标签
2.2、层次选择器
1.后代选择器:在某个元素的后面
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<style>
body p{
background:red;
}
</style>
|

2.子选择器,一代
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<style>
body>p{
background:orange;
}
</style>
|
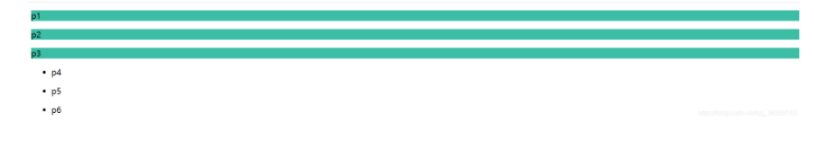
3.相邻的兄弟选择器 同辈
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
<style>
.active+p{
background: red
}
</style>
<body>
<p class="active">p1<p>
<p>p2</p>
</body>
|

4.通用选择器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <style>
.active~p{
background:red;
}
</style>
<body>
<p class="active">p1<p>
<p>p2</p>
</body>
|

HTML
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.active~p{
background: blueviolet;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>p0</p>
<p class="active">p1</p>
<p>p2</p>
<p>p3</p>
<ul>
<li>
<p>p4</p>
</li>
<li>
<p>p5</p>
</li>
<li>
<p>p6</p>
</li>
</ul>
<p>p7</p>
<p>p8</p>
</body>
</html>
|
2.3、结构伪类选择器
伪类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
| <style>
ul li:first-child{
background: aqua;
}
ul li:last-child{
background: blue;
}
p:nth-child(1){
background: orange;
}
p:nth-of-type(2){
background: red;
}
</style>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--避免使用,class,id选择器-->
<style>
ul li:first-child{
background: #a13d30;
}
ul li:last-child{
background: red;
}
p:nth-child(2){
background: blue;
}
p:nth-of-type(1){
background: yellow;
}
a:hover{
background: black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--<h1>h1</h1>-->
<p>p1</p>
<p>p2</p>
<p>p3</p>
<ul>
<li>li1</li>
<li>li2</li>
<li>li3</li>
</ul>
<a href="">链接标签</a>
</body>
</html>
|
2.4、属性选择器(常用)
id + class结合
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.demo a{
display: block;
height: 50px;
width: 50px;
float:left;
border-radius: 10px;
background: blue;
text-align: center;
color: beige;
text-decoration: none;
margin-right: 5px;
font: bold 20px/50px Arial;
}
a[href^="http"]{
background: orange;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="demo">
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" class="links item first" id="first">1</a>
<a href="/adad/faf" class="links item2 first2" >2</a>
<a href="qwe123" class="links item3 first3" >3</a>
<a href="eweqe" class="links item4 first4" >4</a>
<a href="rrrrr" class="links item5 first5" >5</a>
<a href="ttt" class="links item6 first6" >6</a>
<a href="yyy" class="links item7 first7" >7</a>
</p>
</body>
</html>
|

= 绝对等于
*= 包含这个元素
^= 以这个开头
$= 以这个结尾
3、美化网页元素
3.1、为什么要美化网页
- 有效的传递页面信息
- 美化网页,页面漂亮才能吸引客户
- 凸显页面的主题
- 提高用户的体验
span标签:重点要突出的字,使用span标签套起来
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
#title1{
font-size: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
学习语言<span id="title1">JAVA</span>
</body>
</html>
|
font-family:字体系列
font-size:字体大小
font-weight:字体粗细
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| <style>
body{
font-family:楷体;
color:red;
}
h1{
font-size: 50px;
}
.p1{
font-weight:blod;
}
</style>
|
3.2、字体样式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--
font-family:字体
font-size:字体大小
font-weight:字体的粗细
color:字体颜色
-->
<style>
body{
font-family:"Arial Black" ,楷体;
color: #a13d30;
}
h1{
font-size: 50px;
}
.p1{
font-weight: lighter;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>故事介绍</h1>
<p class="p1">
按照表现的内容可分为神话、仙侠、武侠、科幻、悬疑、古传、当代、浪漫青春、游戏竞技等。
</p>
<p>
按照体制可分为章回体小说、日记体小说、书信体小说、自传体小说。按照语言形式可分为文言小说和白话小说。
</p>
<p>
Hooray! It's snowing! It's time to make a snowman.James runs out.
</p>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--字体风格-->
<style>
p{
font: oblique bolder 12px "楷体";
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
按照体制可分为章回体小说、日记体小说、书信体小说、自传体小说。按照语言形式可分为文言小说和白话小说。
</p>
</body>
</html>
font-weight:bolder;
font:oblique bloder 12px "楷体"
|
3.3、文本样式
颜色 –> color, rgb,rgba
文本对齐方式 –> text-align:center
首行缩进 –> text-indent:2em
行高 –> line-height:300px;单行文字上下居中!line-height = height
下划线 –> text-decoration
文本图片水平对齐:vertical-align: middle;
1
2
3
4
| text-decoration:underline
text-decoration:line-through
text-decoration:overline
text-decoration:none
|
图片、文字水平对齐
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
| img,span{vetical-align:middle}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!--
颜色:
单词:#FFFFFF
RGB:0~F ,rgb(0,255,255)
RGBA:A(透明度):0~1,rgba(0,255,255,0.9)
text-indent:段落首行缩进
line-height: 300px;
行高 和 块的高度一致,就可以上下居中
-->
<style>
h1{
color: rgba(0,255,255,0.9);
text-align: center;
}
.p1{
text-indent: 2em;
}
.p3{
background: blueviolet;
height: 300px;
line-height: 50px;
}
.l1{
text-decoration: underline;
}
.l2{
text-decoration: line-through;
}
.l3{
text-decoration: overline;
}
a1{
text-decoration: none;
}
img,span{
vertical-align: middle;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="">a标签去除下划线</a>
<p class="l1">123321</p>
<p class="l2">123321</p>
<p class="l3">123321</p>
<h1>故事介绍</h1>
<p class="p1">
按照表现的内容可分为神话、仙侠、武侠、科幻、悬疑、古传、当代、浪漫青春、游戏竞技等。
</p>
<p>
按照体制可分为章回体小说、日记体小说、书信体小说、自传体小说。按照语言形式可分为文言小说和白话小说。
</p>
<p class="p3">
Hooray! It's snowing! It's time to make a snowman.James runs out.
</p>
<p>
<img src="images/a.png" alt="">
<span>abcdefghijklmnabcdefghijklmn</span>
</p>
</body>
</html>
|
3.4、超链接伪类
超链接伪类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
|
a:link {color: #FF0000}
a:visited {color: #00FF00}
a:hover {color: #FF00FF}
a:active {color: #0000FF}
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
a{
text-decoration: none;
color: #000000;
}
a:hover{
color: burlywood;
font-size: 30px;
}
a:active{
color: #008800;
}
a:link{
color: maroon;
}
a:visited{
color: darkmagenta;
}
#price{
text-shadow: #008800 20px -10px 2px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<a href="#">
<img src="images/a.jpg" alt="">
</a>
<p>
<a href="#">码出高校:Java开发手册</a>
</p>
<p>
<a href="">作者:孤尽老师</a>
</p>
<p id="price">
¥99
</p>
</body>
</html>
<style>
a{
text-decoration:none;
color:#000000;
}
a:hover{
color:orange;
}
a:active{
color:green
}
a:visited{
color:red
}
</style>
|
3.5、阴影
阴影:text-shadow
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
#price{
text-shadow: #008800 20px -10px 2px;
}
text-shadow:5px 5px 5px 颜色
|
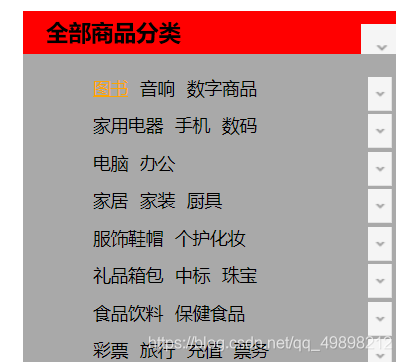
3.6、列表ul li
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>列表样式</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css" type="text/css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="nav">
<h2 class="title">全部商品分类</h2>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">图书</a> <a href="#">音响</a> <a href="#">数字商品</a></li>
<li><a href="#">家用电器</a> <a href="#">手机</a> <a href="#">数码</a></li>
<li><a href="#">电脑</a> <a href="#">办公</a></li>
<li><a href="#">家居</a> <a href="#">家装</a> <a href="#">厨具</a></li>
<li><a href="#">服饰鞋帽</a> <a href="#">个护化妆</a></li>
<li><a href="#">礼品箱包</a> <a href="#">中标</a> <a href="#">珠宝</a></li>
<li><a href="#">食品饮料</a> <a href="#">保健食品</a></li>
<li><a href="#">彩票</a> <a href="#">旅行</a> <a href="#">充值</a> <a href="#">票务</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
#nav{
width: 300px;
background: darkgrey;
}
.title{
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold;
text-indent: 1em;
line-height: 35px;
background: red;
}
/*ul li
list-style:
none:去掉圆点
circle:空心圆
decimal:数字
spuare:正方形
*/
ul{
background: darkgrey;
}
ul li{
height: 30px;
list-style: none;
text-indent: 1em;
}
a{
text-decoration: none;
font-size: 14px;
color: black;
}
a:hover{
color: orange;
text-decoration: underline;
}
/*list-style{
none:去掉原点
circle:空心圆
decimal:数字
square:正方形
}*/
ul li{
height:30px;
list-style:none;
text-indent:1em;
}
a{
text-decoration:none;
font-size:14px;
color:#000;
}
a:hover{
color:orange;
text-decoration:underline/*下划线*/
}
/*放在div中,作为导航栏*/
<div id="nav"></div>
#nav{
width:300px;
}
|
3.7、背景
- 背景颜色:background
- 背景图片
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
div{
width: 1000px;
height: 700px;
border: 1px solid red;
background-image: url("images/tx.jpg");
}
.div1{
background-repeat: repeat-x;
}
.div2{
background-repeat: repeat-y;
}
.div3{
background-repeat: no-repeat;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="div1"></div>
<div class="div2"></div>
<div class="div3"></div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>列表样式</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css" type="text/css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="nav">
<h2 class="title">全部商品分类</h2>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">图书</a> <a href="#">音响</a> <a href="#">数字商品</a></li>
<li><a href="#">家用电器</a> <a href="#">手机</a> <a href="#">数码</a></li>
<li><a href="#">电脑</a> <a href="#">办公</a></li>
<li><a href="#">家居</a> <a href="#">家装</a> <a href="#">厨具</a></li>
<li><a href="#">服饰鞋帽</a> <a href="#">个护化妆</a></li>
<li><a href="#">礼品箱包</a> <a href="#">中标</a> <a href="#">珠宝</a></li>
<li><a href="#">食品饮料</a> <a href="#">保健食品</a></li>
<li><a href="#">彩票</a> <a href="#">旅行</a> <a href="#">充值</a> <a href="#">票务</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
CSS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| #nav{
width: 300px;
background: darkgrey;
}
.title{
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold;
text-indent: 1em;
line-height: 35px;
background: red url("../images/c.jpg") 270px 10px no-repeat;
}
ul li{
height: 30px;
list-style: none;
text-indent: 1em;
background-image: url("../images/b.jpg");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: 236px 2px;
}
a{
text-decoration: none;
font-size: 14px;
color: black;
}
a:hover{
color: orange;
text-decoration: underline;
}
|
1
2
3
4
| background-image:url("");
background-repeat:repeat-x
background-repeat:repeat-y
background-repeat:no-repeat
|
综合使用
1
2
| background:red url("图片相对路劲") 270px 10px no-repeat
background-position:
|
3.8、渐变
线性渐变相关属性:background-image。
线性渐变在线工具:渐变在线工具。
- 线性渐变(Linear Gradients)- 向下/向上/向左/向右/对角方向
- 径向渐变(Radial Gradients)- 由它们的中心定义
3.8.1线性渐变
线性渐变的实例:

语法
1
| background-image: linear-gradient(direction, color-stop1, color-stop2, ...);
|
线性渐变 - 从上到下(默认情况下)
下面的实例演示了从 顶部开始的线性渐变。起点是红色,慢慢过渡到蓝色:
1
2
3
| #grad {
background-image: linear-gradient(#e66465, #9198e5);
}
|
线性渐变 - 从左到右
下面的实例演示了从左边开始的线性渐变。起点是红色,慢慢过渡到黄色:
1
2
3
4
| #grad {
height: 200px;
background-image: linear-gradient(to right, red , yellow);
}
|
线性渐变 - 对角
你可以通过指定水平和垂直的起始位置来制作一个对角渐变。
下面的实例演示了从左上角开始(到右下角)的线性渐变。起点是红色,慢慢过渡到黄色:
1
2
3
4
| #grad {
height: 200px;
background-image: linear-gradient(to bottom right, red, yellow);
}
|
3.8.1.1使用角度
如果你想要在渐变的方向上做更多的控制,你可以定义一个角度,而不用预定义方向(to bottom、to top、to right、to left、to bottom right,等等)。
语法
1
| background-image: linear-gradient(angle, color-stop1, color-stop2);
|
角度是指水平线和渐变线之间的角度,逆时针方向计算。换句话说,0deg 将创建一个从下到上的渐变,90deg 将创建一个从左到右的渐变。

但是,请注意很多浏览器(Chrome、Safari、firefox等)的使用了旧的标准,即 0deg 将创建一个从左到右的渐变,90deg 将创建一个从下到上的渐变。换算公式 90 - x = y 其中 x 为标准角度,y为非标准角度。
下面的实例演示了如何在线性渐变上使用角度:
1
2
3
| #grad {
background-image: linear-gradient(-90deg, red, yellow);
}
|
3.8.1.2使用多个颜色节点
下面的实例演示了如何设置多个颜色节点:
1
2
3
| #grad {
background-image: linear-gradient(red, yellow, green);
}
|
下面的实例演示了如何创建一个带有彩虹颜色和文本的线性渐变:
1
2
3
4
| #grad {
background-image: linear-gradient(to right, red,orange,yellow,green,blue,indigo,violet);
}
|
3.8.1.3使用透明度(transparent)
CSS3 渐变也支持透明度(transparent),可用于创建减弱变淡的效果。
为了添加透明度,我们使用 rgba() 函数来定义颜色节点。rgba() 函数中的最后一个参数可以是从 0 到 1 的值,它定义了颜色的透明度:0 表示完全透明,1 表示完全不透明。
下面的实例演示了从左边开始的线性渐变。起点是完全透明,慢慢过渡到完全不透明的红色:
1
2
3
| #grad {
background-image: linear-gradient(to right, rgba(255,0,0,0), rgba(255,0,0,1));
}
|
3.8.1.4重复的线性渐变
repeating-linear-gradient() 函数用于重复线性渐变:
1
2
3
4
| #grad {
background-image: repeating-linear-gradient(red, yellow 10%, green 20%);
}
|
3.8.2径向渐变
径向渐变由它的中心定义。
为了创建一个径向渐变,你也必须至少定义两种颜色节点。颜色节点即你想要呈现平稳过渡的颜色。同时,你也可以指定渐变的中心、形状(圆形或椭圆形)、大小。默认情况下,渐变的中心是 center(表示在中心点),渐变的形状是 ellipse(表示椭圆形),渐变的大小是 farthest-corner(表示到最远的角落)。
径向渐变的实例:

语法
1
| background-image: radial-gradient(shape size at position, start-color, ..., last-color);
|
径向渐变 - 颜色节点均匀分布(默认情况下)
1
2
3
| #grad {
background-image: radial-gradient(red, yellow, green);
}
|
径向渐变 - 颜色节点不均匀分布
1
2
3
| #grad {
background-image: radial-gradient(red 5%, yellow 15%, green 60%);
}
|
3.8.2.1设置形状
shape 参数定义了形状。它可以是值 circle 或 ellipse。其中,circle 表示圆形,ellipse 表示椭圆形。默认值是 ellipse。
1
2
3
| #grad {
background-image: radial-gradient(circle, red, yellow, green);
}
|
3.8.2.2不同尺寸大小关键字的使用
size 参数定义了渐变的大小。它可以是以下四个值:
- closest-side
- farthest-side
- closest-corner
- farthest-corner
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| #grad1 {
background-image: radial-gradient(closest-side at 60% 55%, red, yellow, black);
}
#grad2 {
background-image: radial-gradient(farthest-side at 60% 55%, red, yellow, black);
}
|
3.8.2.3重复的径向渐变
repeating-radial-gradient() 函数用于重复径向渐变:
1
2
3
| #grad {
background-image: repeating-radial-gradient(red, yellow 10%, green 15%);
}
|
4.1什么是盒子模型

- margin:外边距
- padding:内边距
- border:边框
4.2、边框
border:粗细 样式 颜色
- 边框的粗细
- 边框的样式
- 边框的颜色
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
#box{
width: 300px;
border: 1px solid red;
}
h2{
font-size: 16px;
background-color: cornflowerblue ;
line-height: 30px;
margin: 0px;
}
form{
background: #008800;
}
div:nth-of-type(1) input{
border: 3px solid black;
}
div:nth-of-type(2) input{
border: 3px dashed yellow;
}
div:nth-of-type(3) input{
border: 2px dashed green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<h2>会员登录</h2>
<form action="#">
<div>
<span>用户名:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
<div>
<span>密码:</span>
<input type="password">
</div>
<div>
<span>邮箱:</span>
<input type="text">
</div>
</form>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
盒子的计算方式:你这个元素到底多大?

margin-left/right/top/bottom–>表示四边,可分别设置,也可以同时设置如下
left->左 right->右 top->上 bottom->下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| margin:0 0 0 0
margin:0 auto
margin:4px
margin:10px 20px 30px
|
盒子的计算方式:
margin+border+padding+内容的大小
总结:
body总有一个默认的外边距 margin:0
常见操作:初始化
1
2
3
| margin:0;
padding:0;
text-decoration:none;
|
4.4、圆角边框—-border-radius
border-radius有四个参数(顺时针),左上开始
圆圈:圆角=半径
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 10px solid red;
border-radius: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
#div1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 10px solid red;
border-radius: 100px;
}
#div2{
width: 100px;
height: 50px;
border: 10px solid red;
border-radius: 100px 100px 0 0;
}
#div3{
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
border: 10px solid red;
border-radius: 100px 0 0 0;
}
img{
border-radius: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div1"></div>
<div id="div2"></div>
<div id="div3"></div>
<img src="images/tx.jpg" alt="">
</body>
</html>
|
4.5、盒子阴影
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
img{
border-radius: 50px;
box-shadow: 10px 10px 100px yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div style="width: 500px;display: block;text-align: center ">
<div>
<img src="images/tx.jpg" alt="">
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
源码之家:https://www.mycodes.net/
模板之家:http://www.cssmoban.com/
5、浮动
5.1标准文档流

块级元素:独占一行 h1~h6 、p、div、 列表…
行内元素:不独占一行 span、a、img、strong
注: 行内元素可以包含在块级元素中,反之则不可以。
5.2、display(重要)
- block:块元素
- inline:行内元素
- inline-block:是块元素,但是可以内联,在一行
- none:消失
这也是一种实现行内元素排列的方式,但是我们很多情况用float
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid red;
display: inline-block;
}
span{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid red;
display: inline-block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>div块元素</div>
<span>span行内元素</span>
</body>
</html>
|
QQ会员页面导航练习

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>QQ会员</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css" />
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrap">
<header class="nav-header">
<div class="head-contain">
<a href="" class="top-logo"><img src="img/logo.png" width="145" height="90" /></a>
<nav class="top-nav">
<ul>
<li><a href="">功能特权</a> </li>
<li><a href="">游戏特权</a> </li>
<li><a href="">生活特权</a> </li>
<li><a href="">会员特权</a> </li>
<li><a href="">成长体系</a> </li>
<li><a href="">年费专区</a> </li>
<li><a href="">超级会员</a> </li>
</ul>
</nav>
<div class="top-right">
<a href="">登录</a>
<a href="">开通超级会员</a>
</div>
</div>
</header>
</div>
</body>
</html>
*{
padding:0;
margin: 0;
}
a{
text-decoration: none;
}
.nav-header{
height: 90px;
width: 100%;
background: rgba(0,0,0,.6);
}
.head-contain{
width: 1180px;
height: 90px;
margin: 0 auto;
text-align: center;
}
.top-logo,.top-nav,.top-nav li,.top-right{
height: 90px;
display: inline-block;
vertical-align: top;
}
.top-nav{
margin: 0 48px;
}
.top-nav li{
line-height: 90px;
width: 90px;
}
.top-nav li a{
display: block;
text-align: center;
font-size: 16px;
color: #fff;
}
.top-nav li a:hover{
color: blue;
}
.top-right a{
display: inline-block;
font-size: 16px;
text-align: center;
margin-top: 25px;
border-radius: 35px;
}
.top-right a:first-of-type{
width: 93px;
height: 38px;
line-height: 38px;
color: #fad65c;
border: 1px #fad65c solid;
}
.top-right a:first-of-type:hover{
color: #986b0d;
background: #fad65c;
}
.top-right a:last-of-type{
width: 140px;
height: 40px;
font-weight: 700;
line-height: 40px;
background: #fad65c;
color: #986b0d;
}
.top-right a:last-of-type:hover{
background: #fddc6c;
}
|

5.3、float:left/right左右浮动
clear:both
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css" type="text/css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="father">
<div class="layer01"><img src="images/1.png" alt=""></div>
<div class="layer02"><img src="images/2.png" alt=""></div>
<div class="layer03"><img src="images/3.png" alt=""></div>
<div class="layer04">
浮动的盒子可以向左浮动,也可以向右浮动,知道它的外边缘碰到包含或另一个浮动盒子为止
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
div{
margin: 10px;
padding: 5px;
}
#father{
border: 1px #000 solid;
}
.layer01{
border: 1px #F00 dashed;
display: inline-block;
float: left;/*向左浮动*/
clear: both;/*清楚浮动*/
}
.layer02{
border: 1px #00F dashed;
display: inline-block;
float: left;
clear: both;
}
.layer03{
border: 1px #060 dashed;
display: inline-block;
float: left;
clear: both;
}
.layer04{
border: 1px #666 dashed;
font-size: 12px;
line-height: 23px;
float: left;
clear: both;
}
|
5.4、overflow及父级边框塌陷问题
clear:
right:右侧不允许有浮动元素
left:左侧不允许有浮动元素
both:两侧不允许有浮动元素
none:
解决塌陷问题方案:
方案一:增加父级元素的高度;
1
2
3
4
| #father{
border: 1px #000 solid;
height: 800px;
}
|
方案二:增加一个空的div标签,清除浮动
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css" type="text/css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="father">
<div class="layer01"><img src="images/1.png" alt=""></div>
<div class="layer02"><img src="images/2.png" alt=""></div>
<div class="layer03"><img src="images/3.png" alt=""></div>
<div class="layer04">
浮动的盒子可以向左浮动,也可以向右浮动,知道它的外边缘碰到包含或另一个浮动盒子为止
</div>
<div class="clear"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
div{
margin: 10px;
padding: 5px;
}
#father{
border: 1px #000 solid;
height: 800px;
}
.layer01{
border: 1px #F00 dashed;
display: inline-block;
float: left;/*向左浮动*/
}
.layer02{
border: 1px #00F dashed;
display: inline-block;
float: left;
}
.layer03{
border: 1px #060 dashed;
display: inline-block;
float: right;
}
/*
clear:right;右侧不允许有浮动元素
clear:left; 左侧不允许有浮动元素
clear:both; 两侧不允许有浮动元素
clear:none;
*/
.layer04{
border: 1px #666 dashed;
font-size: 12px;
line-height: 23px;
display: inline-block;
float: right;
clear: left;
}
.clear{
clear: both;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
<div class = "clear"></div>
<style>
.clear{
clear:both;
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
</style>
|
方案三:在父级元素中增加一个overflow:hidden
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| overflow:hidden
overflow:scoll
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
#content{
width: 200px;
height: 150px;
overflow: scroll;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="content">
<img src="images/1.png" alt="">
<p>
某雌性生物醉倒在草地上,路人对其上下其手,并在草地上翻滚,一番折腾后某雌性生物迷迷糊糊醒来步履蹒跚地离开了
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
方案四:父类添加一个伪类:after
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| #father:after{
content:'';
display:block;
clear:both;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
div{
margin: 10px;
padding: 5px;
}
#father{
border: 1px #000 solid;
}
#father:after{
content: '';
display: block;
clear: both;
}
.layer01{
border: 1px #F00 dashed;
display: inline-block;
float: left;
}
.layer02{
border: 1px #00F dashed;
display: inline-block;
float: left;
}
.layer03{
border: 1px #060 dashed;
display: inline-block;
float: right;
}
.layer04{
border: 1px #666 dashed;
font-size: 12px;
line-height: 23px;
display: inline-block;
float: right;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="father">
<div class="layer01"><img src="../lesson06/images/1.png" alt=""></div>
<div class="layer02"><img src="images/2.png" alt=""></div>
<div class="layer03"><img src="images/3.png" alt=""></div>
<div class="layer04">
浮动的盒子可以向左浮动,也可以向右浮动,知道它的外边缘碰到包含或另一个浮动盒子为止
</div>
<div class="clear"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
小结:
- 浮动元素增加空div—-》简单、代码尽量避免空div
- 设置父元素的高度—–》简单,元素假设没有了固定的高度,就会超出
- overflow—-》简单,下拉的一些场景避免使用
- 父类添加一个伪类:after(推荐)—-》写法稍微复杂,但是没有副作用,推荐使用
5.5、display与float对比
- display:方向不可以控制
- float:浮动起来的话会脱离标准文档流,所以要解决父级边框塌陷的问题。
6、定位
6.1、相对定位
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
body{
padding: 20px;
}
div{
margin: 10px;
padding: 5px;
font-size: 12px;
line-height: 25px;
}
#father{
border: 1px solid #666;
}
#first{
background-color: #3cbda6;
border: 1px solid #b27530;
position: relative;
top: -20px;
left: 20px;
}
#second{
background-color: #0000FF;
border: 1px solid #255066;
}
#third{
background-color: #008800;
border: 1px solid #1c6615;
position: relative;
bottom: -20px;
right: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="father">
<div id="first">第一个盒子</div>
<div id="second">第二个盒子</div>
<div id="third">第三个盒子</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
相对定位:positon:relstive;
相对于原来的位置,进行指定的偏移,相对定位的话,它仍然在标准文档流中,原来的位置会被保留
1
2
3
4
| top: -20px;
left: 20px;
bottom: -20px;
right: 20px;
|
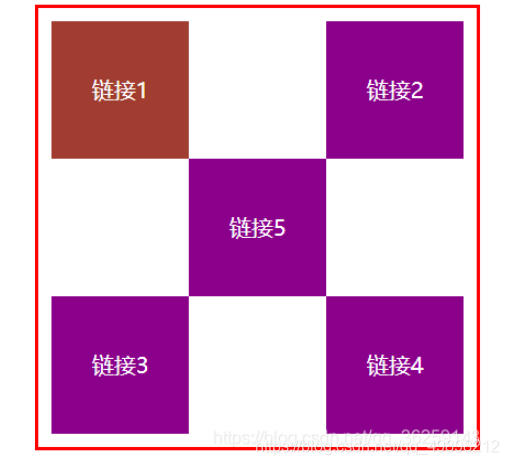
练习题:连接卡
- 使用div和a标签布局页面
- 每个超链接宽度和高度都是100px,背景颜色粉色,鼠标指针移上去变为蓝色
- 使用相对定位改变每个超链接的位置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
#box{
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
padding: 10px;
border: 2px solid red;
}
a{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
text-decoration: none;
background-color: darkmagenta;
line-height: 100px;
text-align: center;
color: white;
display: block;
}
a:hover{
background: #a13d30;
}
.a2,.a4{
position: relative;
left: 200px;
top: -100px;
}
.a5{
position: relative;
left: 100px;
top: -300px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box">
<a class="a1" href="#">链接1</a>
<a class="a2" href="#">链接2</a>
<a class="a3" href="#">链接3</a>
<a class="a4" href="#">链接4</a>
<a class="a5" href="#">链接5</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
6.2、绝对定位-absolute
定位:基于xxx定位,上下左右~
1、没有父级元素定位的前提下,相对于浏览器定位
2、假设父级元素存在定位,我们通常会相对于父级元素进行偏移
3、在父级元素范围内移动
总结:相对一父级或浏览器的位置,进行指定的偏移,绝对定位的话,它不在标准文档流中,原来的位置不会被保留
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
div{
margin: 10px;
padding: 5px;
font-size: 12px;
line-height: 25px;
}
#father{
border: 1px solid #666;
padding: 0;
position: relative;
}
#first{
background-color: #a13d30;
border: 1px dashed #b27530;
}
#second{
background-color: green;
border: 1px dashed #0ece4f;
position: absolute;
right:30px;
top:30px
}
#third{
background-color: red;
border: 1px dashed #ff1b87;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id = "father">
<div id="first">第一个盒子</div>
<div id="second">第二个盒子</div>
<div id="third">第三个盒子</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
6.3、固定定位-fixed
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
body{
height: 1000px;
}
div:nth-of-type(1){
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background:red;
position: absolute;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
div:nth-of-type(2){
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background: yellow;
position: fixed;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>div1</div>
<div>div2</div>
</body>
</html>
|
6.4、z-index

图层~
z-index:默认是0,最高无限~999
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="content">
<ul>
<li><img src="images/bg.jpg" alt=""></li>
<li class="tipText">学习微服务</li>
<li class="tipBg"></li>
<li>时间:2099-01=01</li>
<li>地点:月球一号基地</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
#content{
width: 380;
padding: 0px;
margin: 0px;
overflow: hidden;
font-size: 12px;
line-height: 25px;
border: 1px solid yellow;
}
ul,li{
padding: 0px;
margin: 0px;
list-style: none;
}
/*父级元素相对定位*/
#content ul{
position: relative;
}
.tipText,.tipBg{
position: absolute;
width: 380px;
height: 25px;
top:216px
}
.tipText{
color: white;
z-index: 999;
}
.tipBg{
background: orange;
opacity: 0.5;/*背景透明度*/
filter: alpha(opacity=50);
}
|
7、文字效果
CSS3 文本效果
CSS3中包含几个新的文本特征。
在本章中您将了解以下文本属性:
- text-shadow
- box-shadow
- text-overflow
- word-wrap
- word-break
浏览器支持
| 属性 |
谷歌 |
dege |
火狐 |
Safari |
Opera |
| text-shadow |
4.0 |
10.0 |
3.5 |
4.0 |
9.5 |
| box-shadow |
10.0 4.0 -webkit- |
9.0 |
4.0 3.5 -moz- |
5.1 3.1 -webkit- |
10.5 |
| text-overflow |
4.0 |
6.0 |
7.0 |
3.1 |
11.0 9.0 -o- |
| word-wrap |
23.0 |
5.5 |
3.5 |
6.1 |
12.1 |
| word-break |
4.0 |
5.5 |
15.0 |
3.1 |
15.0 |
CSS3 的文本阴影
CSS3 中,text-shadow属性适用于文本阴影。
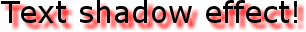
您指定了水平阴影,垂直阴影,模糊的距离,以及阴影的颜色:
1
2
3
4
| h1
{
text-shadow: 5px 5px 5px #FF0000;
}
|
CSS3 box-shadow属性
CSS3 中 CSS3 box-shadow 属性适用于盒子阴影
1
2
3
| div {
box-shadow: 10px 10px 5px #888888;
}
|
接下来给阴影添加颜色
1
2
3
| div {
box-shadow: 10px 10px grey;
}
|
接下来给阴影添加一个模糊效果
1
2
3
| div {
box-shadow: 10px 10px 5px grey;
}
|
你也可以在 ::before 和 ::after 两个伪元素中添加阴影效果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| #boxshadow {
position: relative;
b ox-shadow: 1px 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, .5);
pa dding: 10px;
bac kground: white;
}
#boxshadow img {
width: 100%;
border: 1px solid #8a4419;
border-style: inset;
}
#boxshadow::after {
content: '';
position: absolute;
z-index: -1;
box-shadow: 0 15px 20px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
width: 70%;
left: 15%;
height: 100px;
bottom: 0;
}
|
阴影的一个使用特例是卡片效果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>demo</title>
<style>
div.card {
width: 250px;
box-shadow: 0 4px 8px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2), 0 6px 20px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.19);
text-align: center;
}
div.header {
background-color: #4CAF50;
color: white;
padding: 10px;
font-size: 40px;
}
div.container {
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>卡片</h2>
<p>box-shadow 属性用来可以创建纸质样式卡片:</p>
<div class="card">
<div class="header">
<h1>1</h1>
</div>
<div class="container">
<p>January 1, 2016</p>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>demo</title>
<style>
div.polaroid {
width: 250px;
box-shadow: 0 4px 8px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2), 0 6px 20px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.19);
text-align: center;
}
div.container {
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2> 卡片</h2>
<p>box-shadow属性可以用来创建纸质样式卡片:</p>
<div class="polaroid">
<img src="rock600x400.jpg" alt="Norway" style="width:100%">
<div class="container">
<p>Hardanger, Norway</p>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
CSS3 Text Overflow属性
CSS3文本溢出属性指定应向用户如何显示溢出内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| p.test1 {
white-space: nowrap;
width: 200px;
border: 1px solid #000000;
overflow: hidden;
text-overflow: clip;
}
p.test2 {
white-space: nowrap;
width: 200px;
border: 1px solid #000000;
overflow: hidden;
text-overflow: ellipsis;
}
|
CSS3的换行
如果某个单词太长,不适合在一个区域内,它扩展到外面:
CSS3中,自动换行属性允许您强制文本换行 - 即使这意味着分裂它中间的一个字:
CSS代码如下:
1
| p {word-wrap:break-word;}
|
CSS3 单词拆分换行
CSS3 单词拆分换行属性指定换行规则:
CSS代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| p.test1 {
word-break: keep-all;
}
p.test2 {
word-break: break-all;
}
|
新文本属性
7.1、字体
使用您需要的字体
在新的 @font-face 规则中,您必须首先定义字体的名称(比如 myFirstFont),然后指向该字体文件。
如需为 HTML 元素使用字体,请通过 font-family 属性来引用字体的名称 (myFirstFont):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>DEMO</title>
<style>
@font-face
{
font-family: myFirstFont;
src: url('Sansation_Light.ttf')
,url('Sansation_Light.eot');
}
div
{
font-family:myFirstFont;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p><b>注意:</b> Internet Explorer 9 只支持 .eot 格式的字体.</p>
<div>
使用 CSS3,网站终于可以使用字体以外的预先选择“合法”字体
</div>
</body>
</html>
|
使用粗体文本
您必须添加另一个包含粗体文字的@font-face规则:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>demo</title>
<style>
@font-face
{
font-family: myFirstFont;
src: url(sansation_light.woff);
}
@font-face
{
font-family: myFirstFont;
src: url(sansation_bold.woff);
font-weight:bold;
}
div
{
font-family:myFirstFont;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
使用 CSS3,网站终于可以使用字体以外的预先选择“合法”字体。
</div>
<p><b>注意:</b> Internet Explorer 8以及更早版本的浏览器 @font-face rule.</p>
</body>
</html>
|
该文件”Sansation_Bold.ttf”是另一种字体文件,包含Sansation字体的粗体字。
浏览器使用这一文本的字体系列”myFirstFont”时应该呈现为粗体。
这样你就可以有许多相同的字体@font-face的规则。
CSS3 字体描述
下表列出了所有的字体描述和里面的@font-face规则定义:
| 描述符 |
值 |
描述 |
| font-family |
name |
必需。规定字体的名称。 |
| src |
URL |
必需。定义字体文件的 URL。 |
| font-stretch |
normalcondensedultra-condensedextra-condensedsemi-condensedexpandedsemi-expandedextra-expandedultra-expanded |
可选。定义如何拉伸字体。默认是 “normal”。 |
| font-style |
normalitalicoblique |
可选。定义字体的样式。默认是 “normal”。 |
| font-weight |
normalbold100200300400500600700800900 |
可选。定义字体的粗细。默认是 “normal”。 |
| unicode-range |
unicode-range |
可选。定义字体支持的 UNICODE 字符范围。默认是 “U+0-10FFFF”。 |
8、2D、3D转换
2D 转换
浏览器支持
| 属性 |
 |
|
|
|
|
| transform |
36.0 4.0 -webkit- |
10.0 9.0 -ms- |
16.0 3.5 -moz- |
3.2 -webkit- |
23.0 15.0 -webkit- 12.1 10.5 -o- |
| transform-origin (two-value syntax) |
36.0 4.0 -webkit- |
10.0 9.0 -ms- |
16.0 3.5 -moz- |
3.2 -webkit- |
23.0 15.0 -webkit- 12.1 10.5 -o- |
Internet Explorer 10, Firefox, 和 Opera支持transform 属性.
Chrome 和 Safari 要求前缀 -webkit- 版本.
注意: Internet Explorer 9 要求前缀 -ms- 版本.
2D 转换方法
- translate()
- rotate()
- scale()
- skew()
- matrix()
1
2
3
4
5
6
| div
{
transform: rotate(30deg);
-ms-transform: rotate(30deg);
-webkit-transform: rotate(30deg);
}
|
translate() 方法
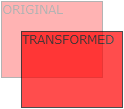
translate()方法,根据左(X轴)和顶部(Y轴)位置给定的参数,从当前元素位置移动。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| div
{
transform: translate(50px,100px);
-ms-transform: translate(50px,100px);
-webkit-transform: translate(50px,100px);
}
|
translate值(50px,100px)是从左边元素移动50个像素,并从顶部移动100像素。
rotate() 方法

rotate()方法,在一个给定度数顺时针旋转的元素。负值是允许的,这样是元素逆时针旋转。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| div
{
transform: rotate(30deg);
-ms-transform: rotate(30deg);
-webkit-transform: rotate(30deg);
}
|
rotate值(30deg)元素顺时针旋转30度。
scale() 方法

scale()方法,该元素增加或减少的大小,取决于宽度(X轴)和高度(Y轴)的参数:
1
2
3
| -ms-transform:scale(2,3);
-webkit-transform: scale(2,3);
transform: scale(2,3);
|
scale(2,3)转变宽度为原来的大小的2倍,和其原始大小3倍的高度。
skew() 方法
1
| transform:skew(<angle> [,<angle>]);
|
包含两个参数值,分别表示X轴和Y轴倾斜的角度,如果第二个参数为空,则默认为0,参数为负表示向相反方向倾斜。
- skewX();表示只在X轴(水平方向)倾斜。
- skewY();表示只在Y轴(垂直方向)倾斜。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| div
{
transform: skew(30deg,20deg);
-ms-transform: skew(30deg,20deg);
-webkit-transform: skew(30deg,20deg);
}
|
skew(30deg,20deg) 元素在 X 轴和 Y 轴上倾斜 20 度 30 度。
matrix() 方法
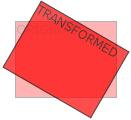
matrix()方法和2D变换方法合并成一个。
matrix 方法有六个参数,包含旋转,缩放,移动(平移)和倾斜功能。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| div
{
transform:matrix(0.866,0.5,-0.5,0.866,0,0);
-ms-transform:matrix(0.866,0.5,-0.5,0.866,0,0);
-webkit-transform:matrix(0.866,0.5,-0.5,0.866,0,0);
}
|
新转换属性
以下列出了所有的转换属性:
2D 转换方法
| 函数 |
描述 |
| matrix(n,n,n,n,n,n) |
定义 2D 转换,使用六个值的矩阵。 |
| translate(x,y) |
定义 2D 转换,沿着 X 和 Y 轴移动元素。 |
| translateX(n) |
定义 2D 转换,沿着 X 轴移动元素。 |
| translateY(n) |
定义 2D 转换,沿着 Y 轴移动元素。 |
| scale(x,y) |
定义 2D 缩放转换,改变元素的宽度和高度。 |
| scaleX(n) |
定义 2D 缩放转换,改变元素的宽度。 |
| scaleY(n) |
定义 2D 缩放转换,改变元素的高度。 |
| rotate(angle) |
定义 2D 旋转,在参数中规定角度。 |
| skew(x-angle,y-angle) |
定义 2D 倾斜转换,沿着 X 和 Y 轴。 |
| skewX(angle) |
定义 2D 倾斜转换,沿着 X 轴。 |
| skewY(angle) |
定义 2D 倾斜转换,沿着 Y 轴。 |
3D 转换
浏览器支持
表格中的数字表示支持该属性的第一个浏览器版本号。
紧跟在 -webkit-, -ms- 或 -moz- 前的数字为支持该前缀属性的第一个浏览器版本号。
| 属性 |
 |
|
|
|
|
| transform |
36.0 12.0 -webkit- |
10.0 |
16.0 10.0 -moz- |
4.0 -webkit- |
23.0 15.0 -webkit- |
| transform-origin (three-value syntax) |
36.0 12.0 -webkit- |
10.0 |
16.0 10.0 -moz- |
4.0 -webkit- |
23.0 15.0 -webkit- |
| transform-style |
36.0 12.0 -webkit- |
11.0 |
16.0 10.0 -moz- |
4.0 -webkit- |
23.0 15.0 -webkit- |
| perspective |
36.0 12.0 -webkit- |
10.0 |
16.0 10.0 -moz- |
4.0 -webkit- |
23.0 15.0 -webkit- |
| perspective-origin |
36.0 12.0 -webkit- |
10.0 |
16.0 10.0 -moz- |
4.0 -webkit- |
23.0 15.0 -webkit- |
| backface-visibility |
36.0 12.0 -webkit- |
10.0 |
16.0 10.0 -moz- |
4.0 -webkit- |
23.0 15.0 -webkit- |
3D 转换方法
rotateX() 方法

rotateX()方法,围绕其在一个给定度数X轴旋转的元素。
1
2
3
4
5
| div
{
transform: rotateX(120deg);
-webkit-transform: rotateX(120deg);
}
|
rotateY() 方法
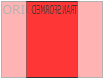
rotateY()方法,围绕其在一个给定度数Y轴旋转的元素
1
2
3
4
5
| div
{
transform: rotateY(130deg);
-webkit-transform: rotateY(130deg);
}
|
转换属性
下表列出了所有的转换属性:
3D 转换方法
| 函数 |
描述 |
| matrix3d(n,n,n,n,n,n, n,n,n,n,n,n,n,n,n,n) |
定义 3D 转换,使用 16 个值的 4x4 矩阵。 |
| translate3d(x,y,z) |
定义 3D 转化。 |
| translateX(x) |
定义 3D 转化,仅使用用于 X 轴的值。 |
| translateY(y) |
定义 3D 转化,仅使用用于 Y 轴的值。 |
| translateZ(z) |
定义 3D 转化,仅使用用于 Z 轴的值。 |
| scale3d(x,y,z) |
定义 3D 缩放转换。 |
| scaleX(x) |
定义 3D 缩放转换,通过给定一个 X 轴的值。 |
| scaleY(y) |
定义 3D 缩放转换,通过给定一个 Y 轴的值。 |
| scaleZ(z) |
定义 3D 缩放转换,通过给定一个 Z 轴的值。 |
| rotate3d(x,y,z,angle) |
定义 3D 旋转。 |
| rotateX(angle) |
定义沿 X 轴的 3D 旋转。 |
| rotateY(angle) |
定义沿 Y 轴的 3D 旋转。 |
| rotateZ(angle) |
定义沿 Z 轴的 3D 旋转。 |
| perspective(n) |
定义 3D 转换元素的透视视图。 |
9、过渡
CSS3 过渡
CSS3中,我们为了添加某种效果可以从一种样式转变到另一个的时候,无需使用Flash动画或JavaScript。
浏览器支持
表格中的数字表示支持该属性的第一个浏览器版本号。
紧跟在 -webkit-, -ms- 或 -moz- 前的数字为支持该前缀属性的第一个浏览器版本号。
它是如何工作?
CSS3 过渡是元素从一种样式逐渐改变为另一种的效果。
要实现这一点,必须规定两项内容:
1
2
3
4
5
| div
{
transition: width 2s;
-webkit-transition: width 2s;
}
|
注意: 如果未指定的期限,transition将没有任何效果,因为默认值是0。
指定的CSS属性的值更改时效果会发生变化。一个典型CSS属性的变化是用户鼠标放在一个元素上时:
1
2
3
4
| div:hover
{
width:300px;
}
|
注意: 当鼠标光标移动到该元素时,它逐渐改变它原有样式
多项改变
要添加多个样式的变换效果,添加的属性由逗号分隔:
1
2
3
4
5
| div
{
transition: width 2s, height 2s, transform 2s;
-webkit-transition: width 2s, height 2s, -webkit-transform 2s;
}
|
过渡属性
下表列出了所有的过渡属性:
下面的两个例子设置所有过渡属性:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>demo</title>
<style>
div
{
width:100px;
height:100px;
background:red;
transition-property:width;
transition-duration:1s;
transition-timing-function:linear;
transition-delay:2s;
-webkit-transition-property:width;
-webkit-transition-duration:1s;
-webkit-transition-timing-function:linear;
-webkit-transition-delay:2s;
}
div:hover
{
width:200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p><b>注意:</b>该实例无法在 Internet Explorer 9 及更早 IE 版本上工作。</p>
<div></div>
<p>鼠标移动到 div 元素上,查看过渡效果。</p>
<p><b>注意:</b> 过渡效果需要等待两秒后才开始。</p>
</body>
</html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>demo</title>
<style>
div
{
width:100px;
height:100px;
background:red;
transition:width 1s linear 2s;
-webkit-transition:width 1s linear 2s;
}
div:hover
{
width:200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p><b>注意:</b>该实例无法在 Internet Explorer 9 及更早 IE 版本上工作。</p>
<div></div>
<p>鼠标移动到 div 元素上,查看过渡效果。</p>
<p><b>注意:</b> 过渡效果需要等待两秒后才开始。</p>
</body>
</html>
|
10、动画
CSS3 动画
CSS3 可以创建动画,它可以取代许多网页动画图像、Flash 动画和 JavaScript 实现的效果。
CSS3 @keyframes 规则
要创建 CSS3 动画,你需要了解 @keyframes 规则。
@keyframes 规则是创建动画。
@keyframes 规则内指定一个 CSS 样式和动画将逐步从目前的样式更改为新的样式。
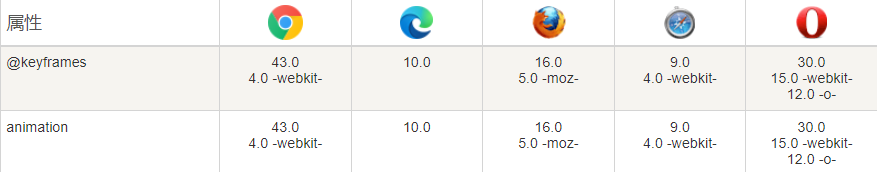
浏览器支持
表格中的数字表示支持该属性的第一个浏览器版本号。
紧跟在 -webkit-, -ms- 或 -moz- 前的数字为支持该前缀属性的第一个浏览器版本号。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @keyframes myfirst
{
from {background: red;}
to {background: yellow;}
}
@-webkit-keyframes myfirst /* Safari 与 Chrome */
{
from {background: red;}
to {background: yellow;}
}
|
CSS3 动画
当在 @keyframes 创建动画,把它绑定到一个选择器,否则动画不会有任何效果。
指定至少这两个CSS3的动画属性绑定向一个选择器:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>demo</title>
<style>
div
{
width:100px;
height:100px;
background:red;
animation:myfirst 5s;
-webkit-animation:myfirst 5s;
}
@keyframes myfirst
{
from {background:red;}
to {background:yellow;}
}
@-webkit-keyframes myfirst /* Safari and Chrome */
{
from {background:red;}
to {background:yellow;}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p><b>注意:</b> 该实例在 Internet Explorer 9 及更早 IE 版本是无效的。</p>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
|
注意: 您必须定义动画的名称和动画的持续时间。如果省略的持续时间,动画将无法运行,因为默认值是0。
CSS3动画是什么?
动画是使元素从一种样式逐渐变化为另一种样式的效果。
您可以改变任意多的样式任意多的次数。
请用百分比来规定变化发生的时间,或用关键词 “from” 和 “to”,等同于 0% 和 100%。
0% 是动画的开始,100% 是动画的完成。
为了得到最佳的浏览器支持,您应该始终定义 0% 和 100% 选择器。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>菜鸟教程(runoob.com)</title>
<style>
div
{
width:100px;
height:100px;
background:red;
animation:myfirst 5s;
-moz-animation:myfirst 5s;
-webkit-animation:myfirst 5s;
-o-animation:myfirst 5s;
}
@keyframes myfirst
{
0% {background:red;}
25% {background:yellow;}
50% {background:blue;}
100% {background:green;}
}
@-moz-keyframes myfirst /* Firefox */
{
0% {background:red;}
25% {background:yellow;}
50% {background:blue;}
100% {background:green;}
}
@-webkit-keyframes myfirst /* Safari and Chrome */
{
0% {background:red;}
25% {background:yellow;}
50% {background:blue;}
100% {background:green;}
}
@-o-keyframes myfirst /* Opera */
{
0% {background:red;}
25% {background:yellow;}
50% {background:blue;}
100% {background:green;}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<p><b>注释:</b>当动画完成时,会变回初始的样式。</p>
<p><b>注意:</b> 该实例在 Internet Explorer 9 及更早 IE 版本是无效的。</p>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>demo</title>
<style>
div
{
width:100px;
height:100px;
background:red;
position:relative;
animation:myfirst 5s;
-webkit-animation:myfirst 5s;
}
@keyframes myfirst
{
0% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
25% {background:yellow; left:200px; top:0px;}
50% {background:blue; left:200px; top:200px;}
75% {background:green; left:0px; top:200px;}
100% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
@-webkit-keyframes myfirst /* Safari and Chrome */
{
0% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
25% {background:yellow; left:200px; top:0px;}
50% {background:blue; left:200px; top:200px;}
75% {background:green; left:0px; top:200px;}
100% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p><b>注意:</b> 该实例在 Internet Explorer 9 及更早 IE 版本是无效的。</p>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
|
CSS3的动画属性
下面的表格列出了 @keyframes 规则和所有动画属性:
下面两个例子设置所有动画属性:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>demo</title>
<style>
div
{
width:100px;
height:100px;
background:red;
position:relative;
animation-name:myfirst;
animation-duration:5s;
animation-timing-function:linear;
animation-delay:2s;
animation-iteration-count:infinite;
animation-direction:alternate;
animation-play-state:running;
-webkit-animation-name:myfirst;
-webkit-animation-duration:5s;
-webkit-animation-timing-function:linear;
-webkit-animation-delay:2s;
-webkit-animation-iteration-count:infinite;
-webkit-animation-direction:alternate;
-webkit-animation-play-state:running;
}
@keyframes myfirst
{
0% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
25% {background:yellow; left:200px; top:0px;}
50% {background:blue; left:200px; top:200px;}
75% {background:green; left:0px; top:200px;}
100% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
@-webkit-keyframes myfirst /* Safari and Chrome */
{
0% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
25% {background:yellow; left:200px; top:0px;}
50% {background:blue; left:200px; top:200px;}
75% {background:green; left:0px; top:200px;}
100% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p><b>注意:</b> 该实例在 Internet Explorer 9 及更早 IE 版本是无效的。</p>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>demo</title>
<style>
div
{
width:100px;
height:100px;
background:red;
position:relative;
animation:myfirst 5s linear 2s infinite alternate;
-moz-animation:myfirst 5s linear 2s infinite alternate;
-webkit-animation:myfirst 5s linear 2s infinite alternate;
-o-animation:myfirst 5s linear 2s infinite alternate;
}
@keyframes myfirst
{
0% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
25% {background:yellow; left:200px; top:0px;}
50% {background:blue; left:200px; top:200px;}
75% {background:green; left:0px; top:200px;}
100% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
@-moz-keyframes myfirst /* Firefox */
{
0% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
25% {background:yellow; left:200px; top:0px;}
50% {background:blue; left:200px; top:200px;}
75% {background:green; left:0px; top:200px;}
100% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
@-webkit-keyframes myfirst /* Safari and Chrome */
{
0% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
25% {background:yellow; left:200px; top:0px;}
50% {background:blue; left:200px; top:200px;}
75% {background:green; left:0px; top:200px;}
100% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
@-o-keyframes myfirst /* Opera */
{
0% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
25% {background:yellow; left:200px; top:0px;}
50% {background:blue; left:200px; top:200px;}
75% {background:green; left:0px; top:200px;}
100% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p><b>注意:</b> 该实例在 Internet Explorer 9 及更早 IE 版本是无效的。</p>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
|